Why does the need for a lightning network arise?
When Satoshi Nakamoto first described Bitcoin in a whitepaper in 2008, the creator used the phrase “peer-to-peer electronic cash.” The ideology behind proposing this currency was that one day, it would become a popular way to pay for goods and services online on a global scale. But the shift in Bitcoin’s valuation over the years has changed the narrative.
Some consider it “digital gold” or a way to resist wealth from market inflation. It is designed so that two strangers from anywhere in the world can securely send or receive funds without any intermediary, such as a credit card or payment processor bank or company. Such transactions do need a mechanism to function, and the solution to this was mining– a time-consuming process.
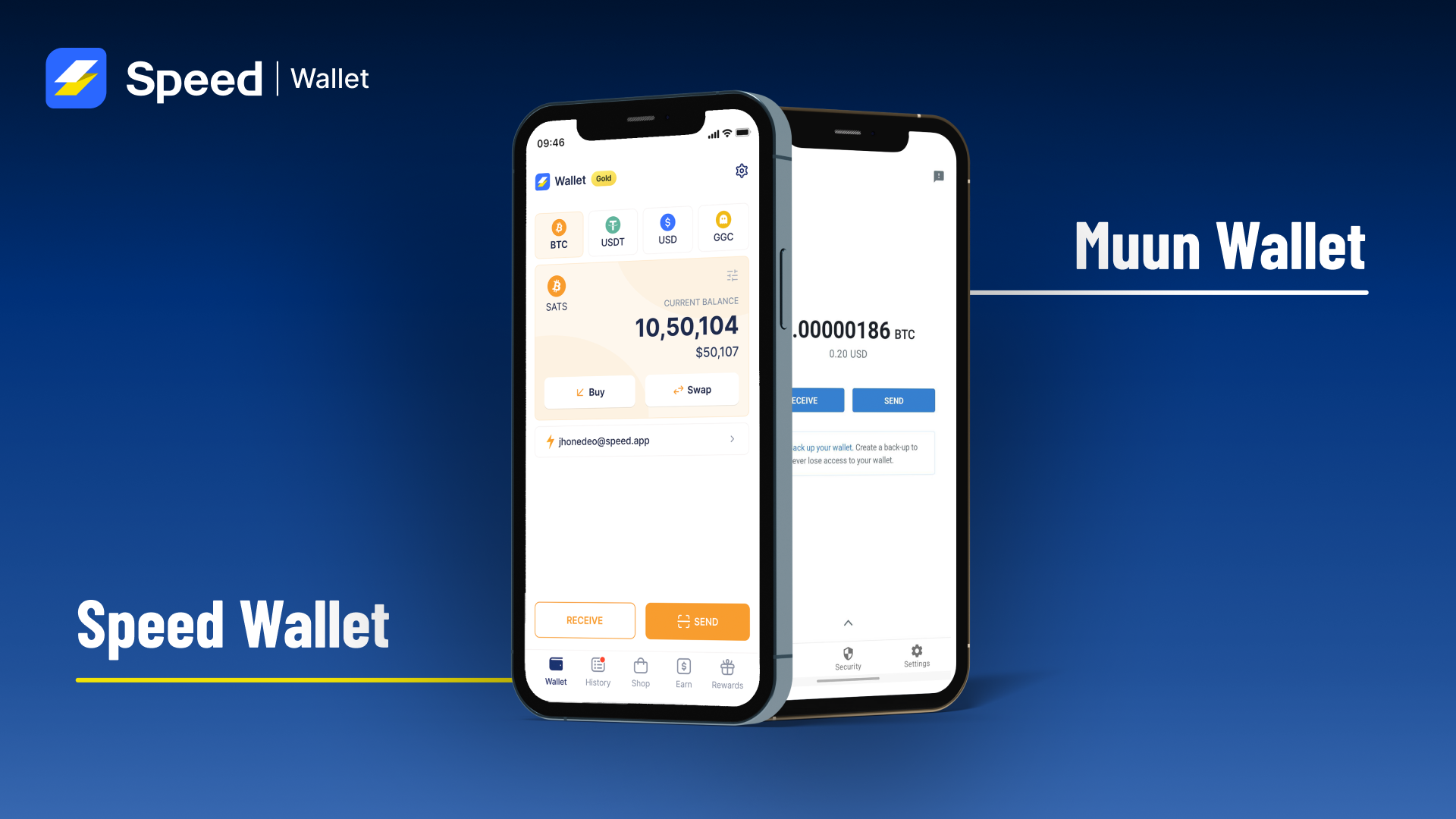
To control all these malfunctions and make the Bitcoin function smoothly, ‘Lightning Network‘ was invented. It helps in processing the transactions “off-chain,” which is cost-saving and quicker than the Bitcoins core blockchain. LN transactions are less energy-intensive than on the main blockchain.
The main Bitcoin blockchain (layer 1) can handle less than 10 transactions/sec. In contrast, the LN (layer 2) can handle millions of transactions/sec. With all such needs apart, global business models that can function on a faster mode of decentralized transactions are also in demand.